- May 2, 2022
- Posted by: Admin
- Category: Case Study, News, Research

A lot of people have the idea with the terms data privacy and data security are synonyms. When it comes to data privacy vs data security, the phrases are commonly used interchangeably. Are these, nevertheless, synonyms, or do they refer to two distinct concepts?
Data security is no longer an option, but a necessity in a cyberspace world. Data privacy and data security should be the top priority for any business. Before we jump into the differentiating factors it is crucial to understand the general understanding about data privacy and data security.
What is data security?
In order to tell the difference, we have to ask ourselves what security means for us? Quite simply, it could be health insurance or steady employment. We use data security tools in our computer system to protect from unauthorized access or attacks. This encompasses any kind of device, server or network.
Data security imparts confidentiality, availability and integrity of data. It focuses on the physical security of premises, logical security of data and digitalized information.
What is data privacy?
Data privacy refers to how personal information is handled, processed, stored, and used. It’s all about people’s privacy rights when it comes to their personal information. In the same way, data privacy relates to appropriate use and control of data.
- What data is collected?
- How is the data stored?
- Who can access the data?
These questions can help you figure out how to protect sensitive data while yet allowing it to be beneficial to your organization.
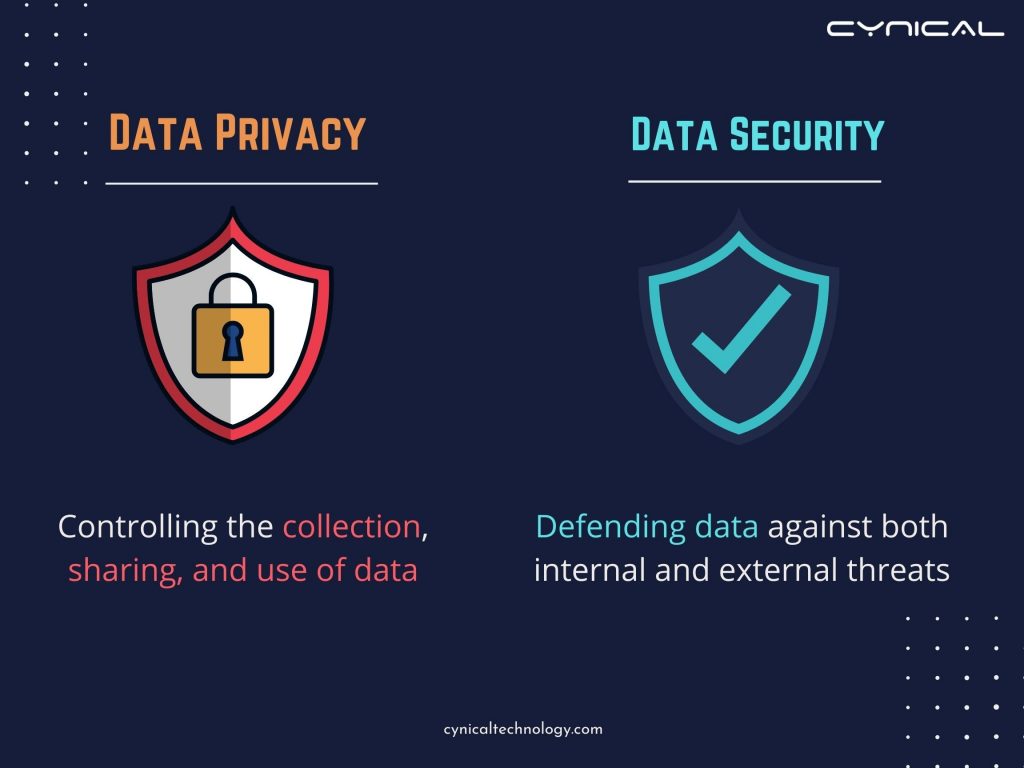
How to tell the difference between data privacy and data security?
The primary distinction between data security and data privacy is that privacy ensures the proper use and control of data whereas data security relates to confidentiality, availability, and integrity of data.
Data security is the process of safeguarding digital data throughout its lifecycle against unwanted access, corruption, or theft.
Data security mostly focuses on keeping data secure. Whether or not the underlying infrastructure is secure. For example; Companies adapt MFA (Multifactor Authentication) to guarantee data security.
While Data privacy, often known as information privacy, is a subcategory of data protection that includes the ethical and legal responsibility to safeguard access to personally identifiable information (PII).
Here are a few cases of data privacy regulations, as well as who they affect and what they require in general. Many of these laws incorporate data security standards in addition to data privacy requirements.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
GDPR and HIPAA regulations place a strong emphasis on protecting the privacy of personally identifiable information.
Typically, a business would appoint a data protection officer who will be in charge of identifying the data that needs to be safeguarded and developing a set of procedures to ensure that the data can be recovered if it is accidentally lost, rewritten, or corrupted.
Summary
Because security and privacy are intertwined, you must develop the practice of safeguarding both. It may appear to be a time-consuming and daunting task, but understanding the interconnection between the terms helps businesses to maintain customers’ trust and use data to make a positive impact.
