- September 29, 2024
- Posted by: Bikash Sharma
- Category: Awareness, News
Nepal’s Journey in Cybersecurity: Progress from 2020 to 2024
Nepal’s Cybersecurity Rise: 2020 to 2024
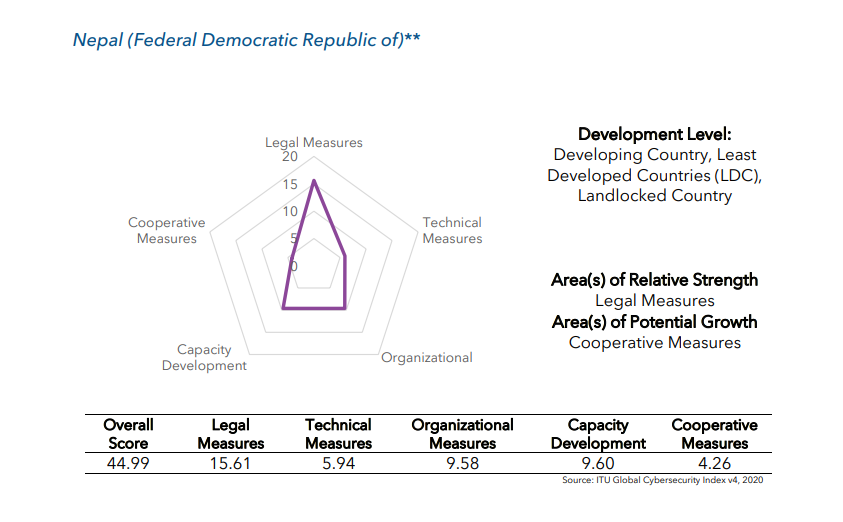
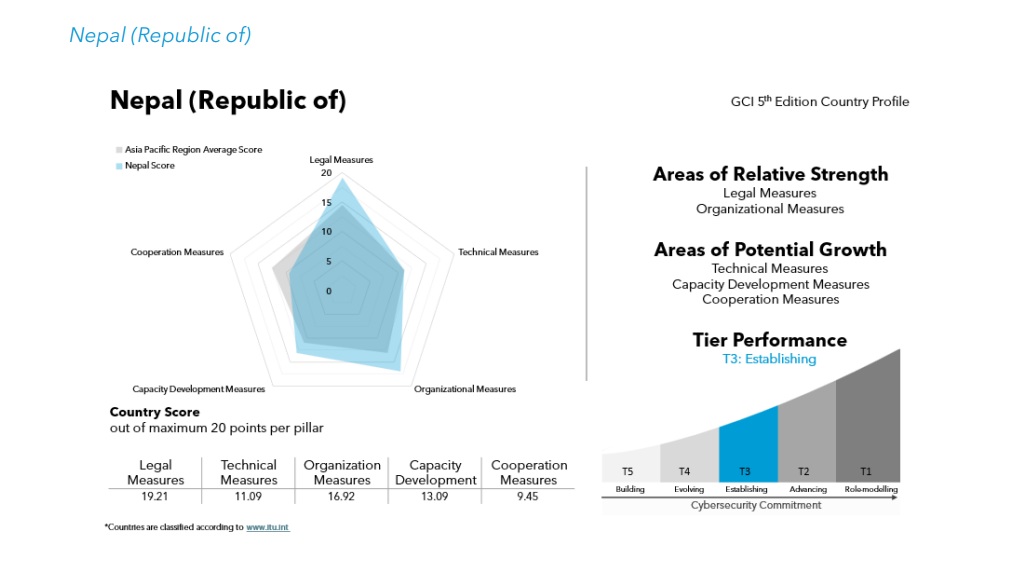
Between 2020 and 2024, Nepal’s performance in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) saw impressive improvement. Back in 2020, Nepal had a modest score of 44.99, reflecting a nation still building the basic foundation of cybersecurity practices. However, by 2024, Nepal’s score surged to 69.76—a stunning 55% increase. This growth is a clear sign of how seriously the country is taking the protection of its digital infrastructure, data, and users.
Cybersecurity Index Nepal Year 2020
Cybersecurity Index Nepal Year 2024
Key Areas of Growth:
Let’s break down how Nepal improved across different aspects of cybersecurity:
- Legal Measures: In the last four years, Nepal has strengthened its laws and regulations on cybersecurity by 22%. This includes better policies to fight cybercrime, protect data, and regulate how businesses handle personal information.
- Technical Measures: Nepal saw the most dramatic progress here, with an 87% improvement. The country is now better equipped with the technology and tools needed to respond to cyberattacks, secure its networks, and safeguard sensitive information.
- Organizational Measures: There has also been a 76% growth in how well Nepal organizes its cybersecurity efforts. This includes the creation of special government agencies that focus solely on cybersecurity, helping the nation be more organized and proactive when it comes to cyber threats.
- Capacity Development: Nepal has been working hard to educate its people about cybersecurity. This effort increased by 36% since 2020, showing that more Nepali professionals are receiving the training they need to keep the country’s digital spaces safe.
- Cooperation Measures: Though there is still work to be done, Nepal improved its international cooperation efforts by 11%. This means the country is now more engaged in global cybersecurity discussions and is working together with other nations to tackle international cyber threats.
Tier Performance: Where Does Nepal Stand in the Asia-Pacific?
The Global Cybersecurity Index also groups countries into performance tiers, which reflect how developed a country’s cybersecurity systems are. According to the most recent report, Nepal is ranked in Tier 3: Establishing. This means Nepal has made good progress but still has work to do to become one of the top performers in cybersecurity.
In Tier 3, Nepal is joined by countries like Bhutan, Myanmar, and New Zealand. These countries are building their cybersecurity frameworks and have shown dedication but are still working towards becoming advanced in the field. Countries like Australia, India, and Japan, which fall under Tier 1: Role-Modelling, are examples of nations with highly developed and sophisticated cybersecurity systems. These nations have not only implemented strong measures but are also considered role models in how they handle cyber risks.
For Nepal to move up to Tier 2: Advancing or Tier 1, it will need to continue improving its technical measures, boost international partnerships, and enhance its capacity-building efforts.
How Nepal Compares to Its Neighbors
When comparing Nepal’s progress to other countries in the Asia-Pacific, it’s clear that the nation is steadily catching up to regional leaders. For example:
- India, in Tier 1, is already seen as a cybersecurity leader in Asia. It has advanced measures in place, with strong cyber laws and technical capabilities.
- Bangladesh and Pakistan, like India, also rank in Tier 1, meaning they are further ahead in terms of cybersecurity readiness.
Nepal’s progress, while slower, has been steady, and with continued efforts, the country can rise further in the rankings. The key for Nepal now is to focus on sustained development in technical infrastructure and education.
Strengths and Areas for Improvement
Nepal has clearly made great strides in cybersecurity, but there’s still work to be done.
- Strengths: Nepal’s legal and organizational improvements have laid a strong foundation. The creation of dedicated cybersecurity agencies and the implementation of new policies have helped boost the country’s preparedness for future cyberattacks.
- Technical Growth: The most impressive area of growth has been in Nepal’s technical capabilities, with an 87% increase in four years. This reflects better technology and expertise to secure the country’s digital infrastructure. However, even with this progress, Nepal still has room to enhance its cybersecurity tools to meet the highest global standards.
- Challenges: One of the areas where Nepal still needs to focus is international cooperation. Cybersecurity is a global issue, and Nepal will need to strengthen its ties with other nations, sharing knowledge and learning from more advanced countries. Additionally, continuing to build capacity by training more cybersecurity professionals will be critical for the nation’s future progress.
The Path Forward for Nepal
The path forward for Nepal is clear: continue building on its current momentum and focusing on areas that still need improvement. Technical development is essential for the country to defend against more sophisticated threats. Cyber threats are becoming more advanced every year, and Nepal needs to keep pace by investing in cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies and tools.
Another critical step for Nepal is to continue educating its workforce. By developing more cybersecurity professionals, the country can ensure that it has the human resources necessary to manage and mitigate threats. This also includes raising awareness among businesses and the general public about how they can protect themselves online.
Moreover, global cooperation will play a big role. By engaging with international cybersecurity organizations, Nepal can learn from global best practices and participate in shared efforts to combat cross-border cybercrime.
Conclusion: A Promising Future
Nepal’s cybersecurity journey from 2020 to 2024 has been nothing short of impressive. With a 55% improvement in its overall Global Cybersecurity Index score, Nepal has demonstrated its commitment to becoming a safer, more secure digital nation. While the country is still in the Establishing phase, the foundation has been laid for continued progress.
As Nepal looks to the future, the focus should be on building stronger technical measures, expanding its cybersecurity workforce, and forging closer ties with international partners. With these efforts, Nepal can not only climb higher in global cybersecurity rankings but also ensure a safer digital environment for its citizens and businesses alike.
You can explore the full report here: ITU Global Cybersecurity Index.